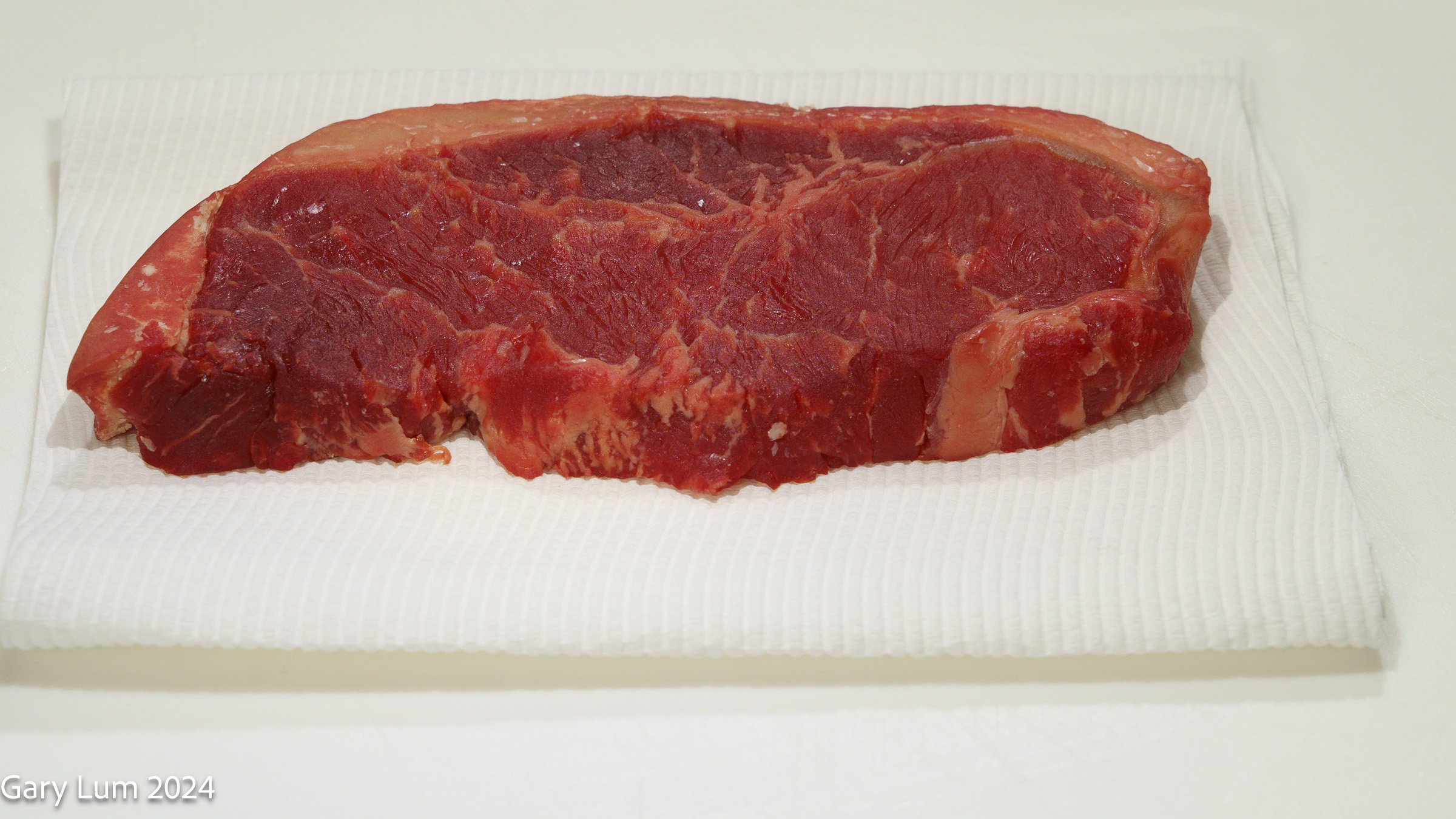
Porterhouse Steak Description: Porterhouse steak is a premium cut of beef that is known for its flavour and tenderness [1]. This steak is cut from the rear end of the short loin and includes a portion of the tenderloin and the top loin, making it a combination of two highly desirable cuts of beef [4]. It’s often referred to as a two-in-one steak because it combines a strip cut and a tenderloin cut, divided by a T-shaped bone [3]. The porterhouse is a composite steak that’s derived from the point where the tenderloin and top loin meet [1]. If you order a porterhouse, expect decent portions [1].
Names in Other Countries: In Australia, we call a porterhouse steak a boneless sirloin steak, but pretty much everywhere else in the world, a porterhouse comes on the bone [10]. In some parts of the world, it’s known as a “T-bone” [11]. In Italy, a Porterhouse steak is sometimes called a Fiorentina steak [11].
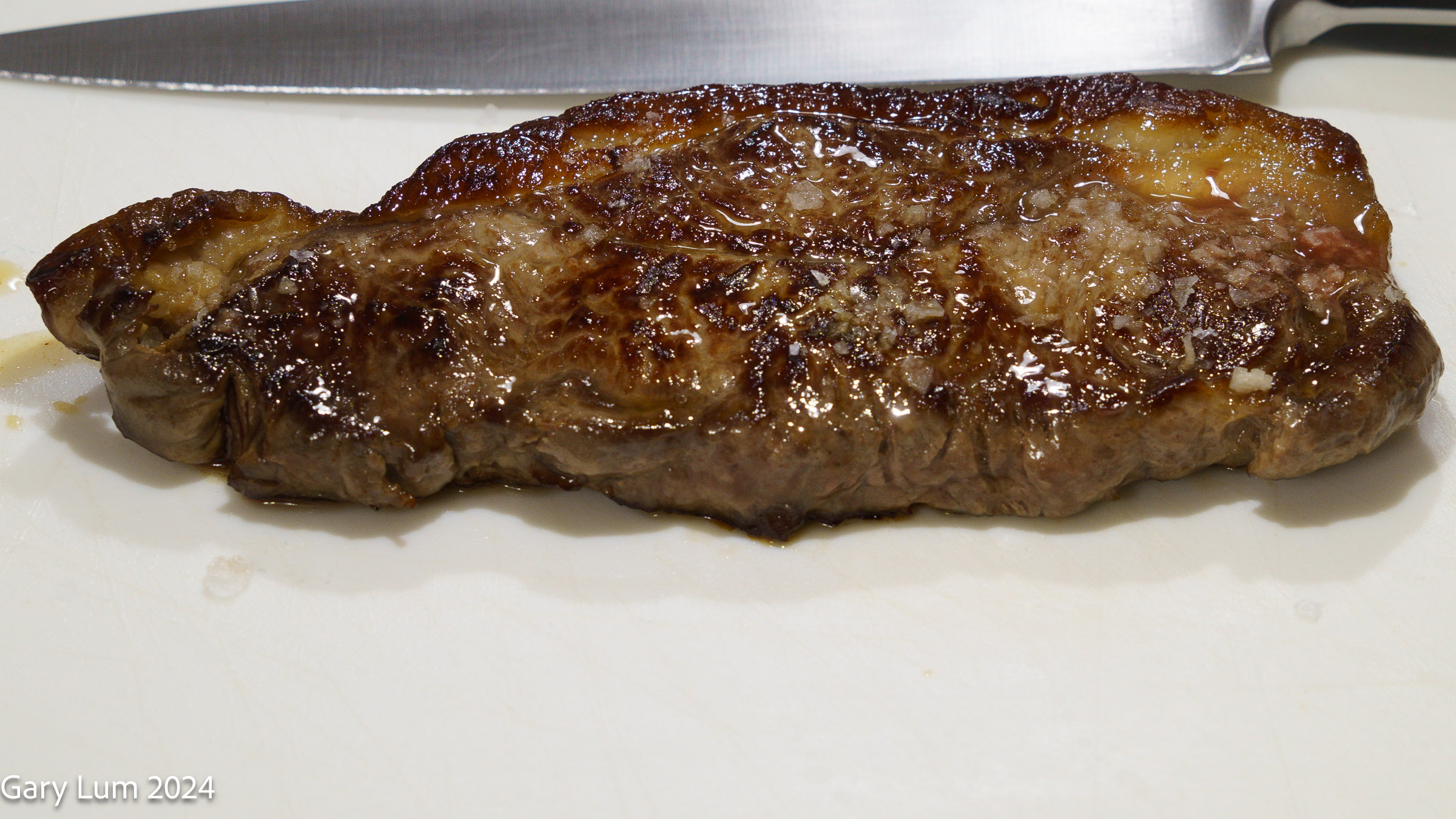
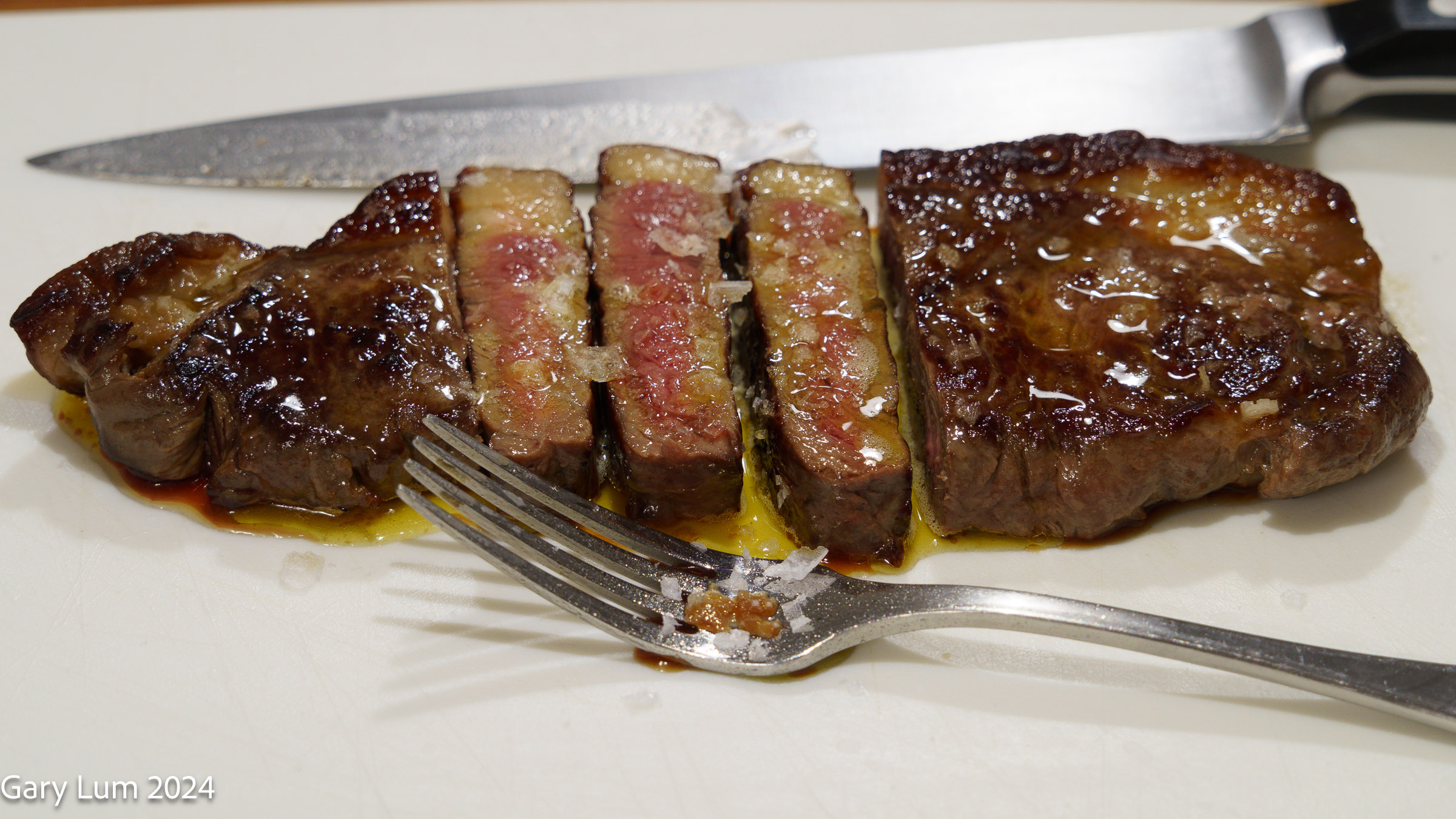
Cooking and Eating Characteristics: Porterhouse steak offers a unique flavour profile, combining the tenderness of the tenderloin with the rich, beefy flavour of a strip steak [2]. For the most authentic steakhouse flavour, cook your porterhouse on the grill [1]. But you can also get great results with a hot cast iron skillet on the stovetop [1]. Use a generous amount of salt and try not to cook the steak beyond medium, or 57 °C, at the most [1].
Nutrient Values: A typical serving of porterhouse steak (about 100 grams) contains [6] [7]:
- Calories: 139
- Total Fat: 5.3 g
- Saturated Fat: 2 g
- Cholesterol: 57 mg
- Sodium: 43 mg
- Potassium: 266 mg
- Carbohydrates: 0 g
- Protein: 22.7 g
- Zinc: 2.53 mg
- Vitamin B12, niacin, vitamin B-6, riboflavin and traces of many other vitamins [8].
Health Benefits: Porterhouse steak is rich in protein, offering close to 23 grams in a 100-gram serving [7]. It’s also full of nutrients and vitamins that are essential to your body, such as Vitamin B12, Vitamin B6, and Iron [7].









Ask a question or make a comment